EzeCHieL
EzeCHiel aims at assisting healthcare practitioners and pharmacologists with the interpretation of medical drug concentration measurements and the adjustment of dosages (also called Therapeutic Drug Monitoring – TDM).
The main features of EzeCHiel are:
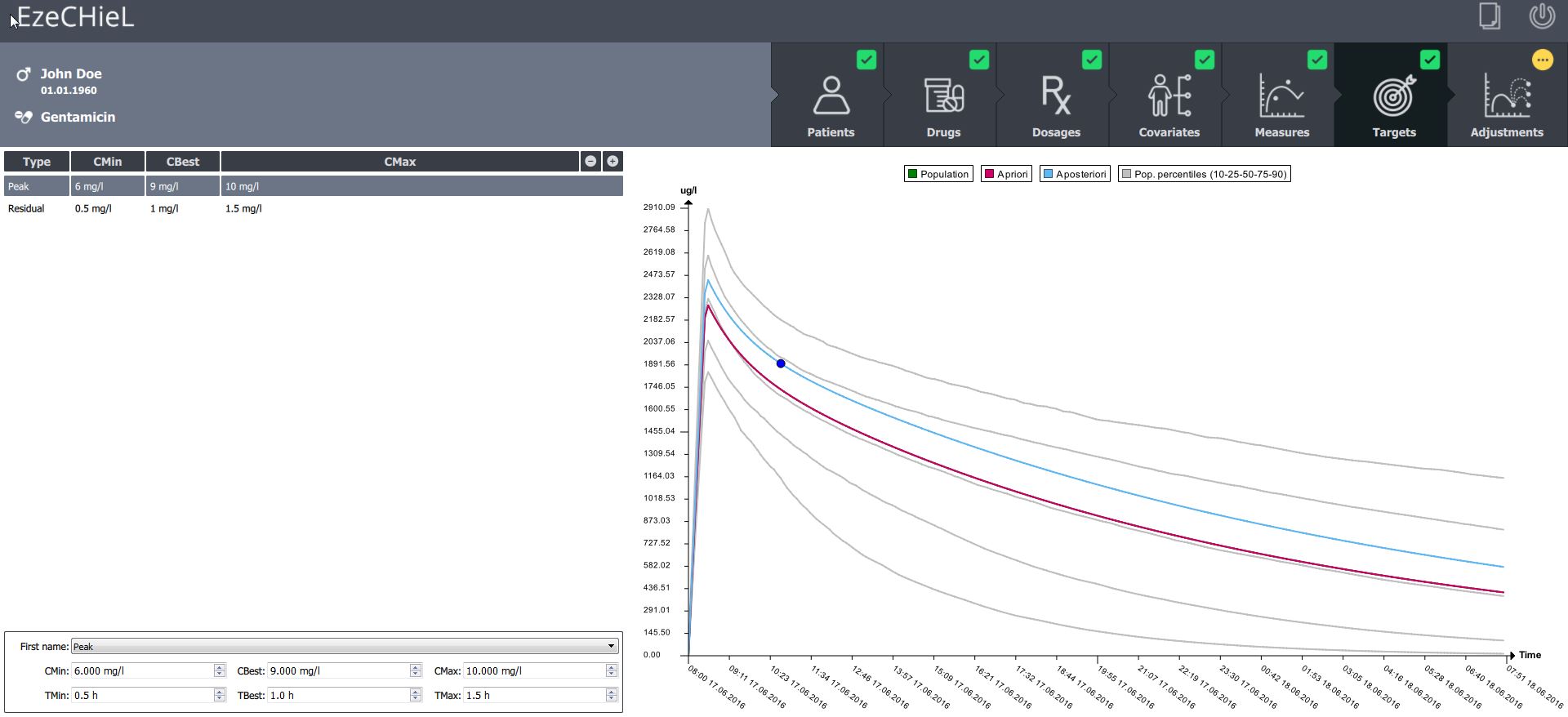
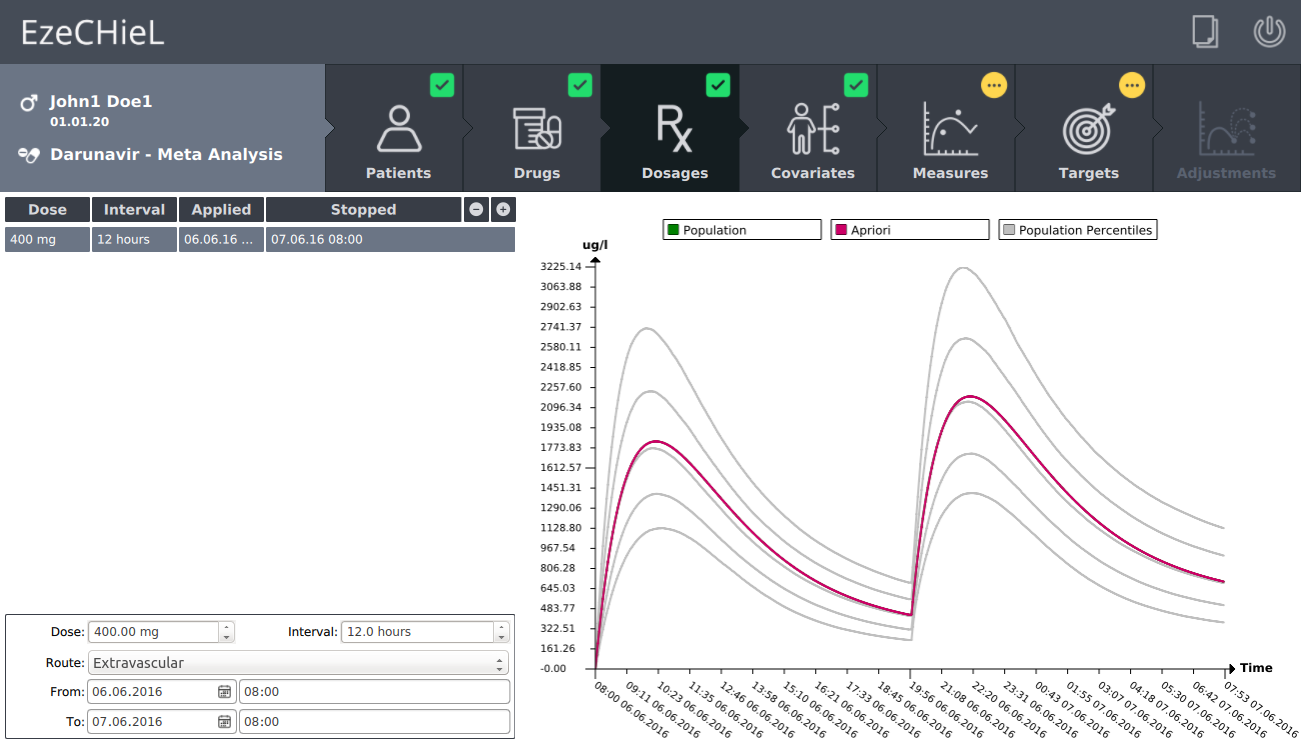
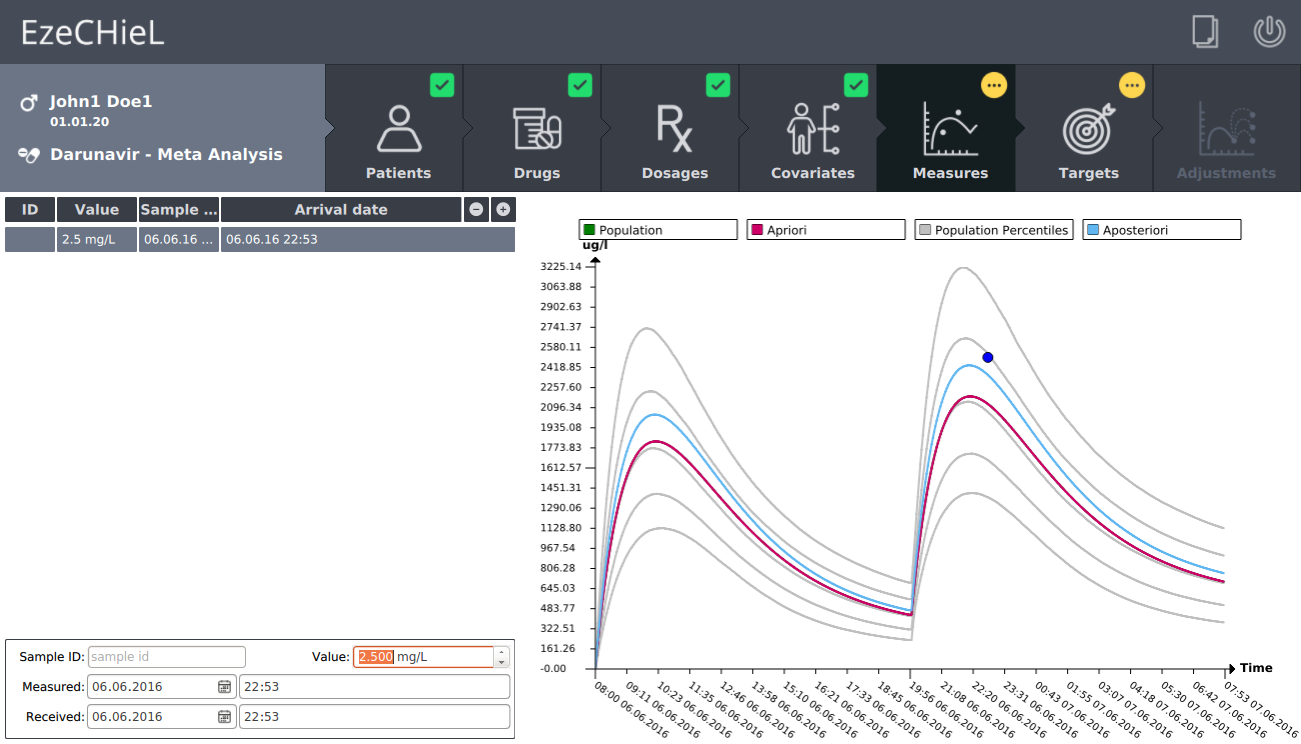
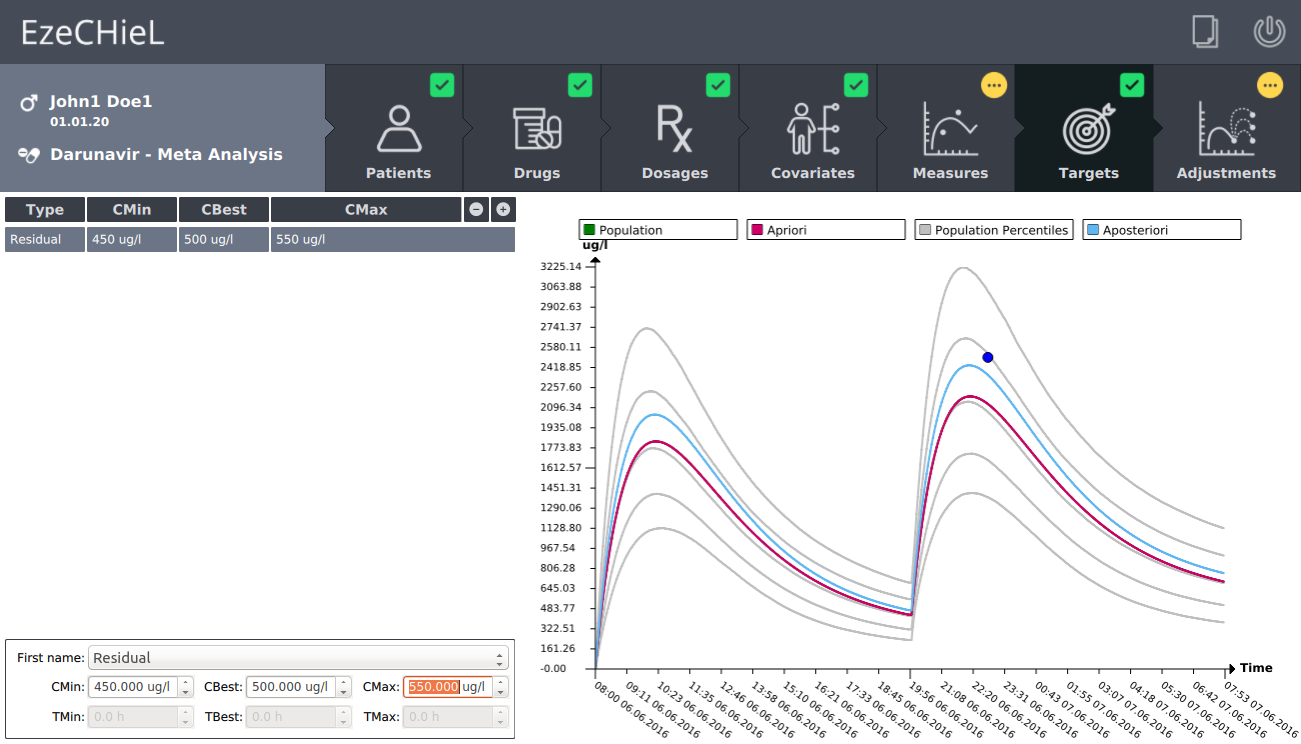
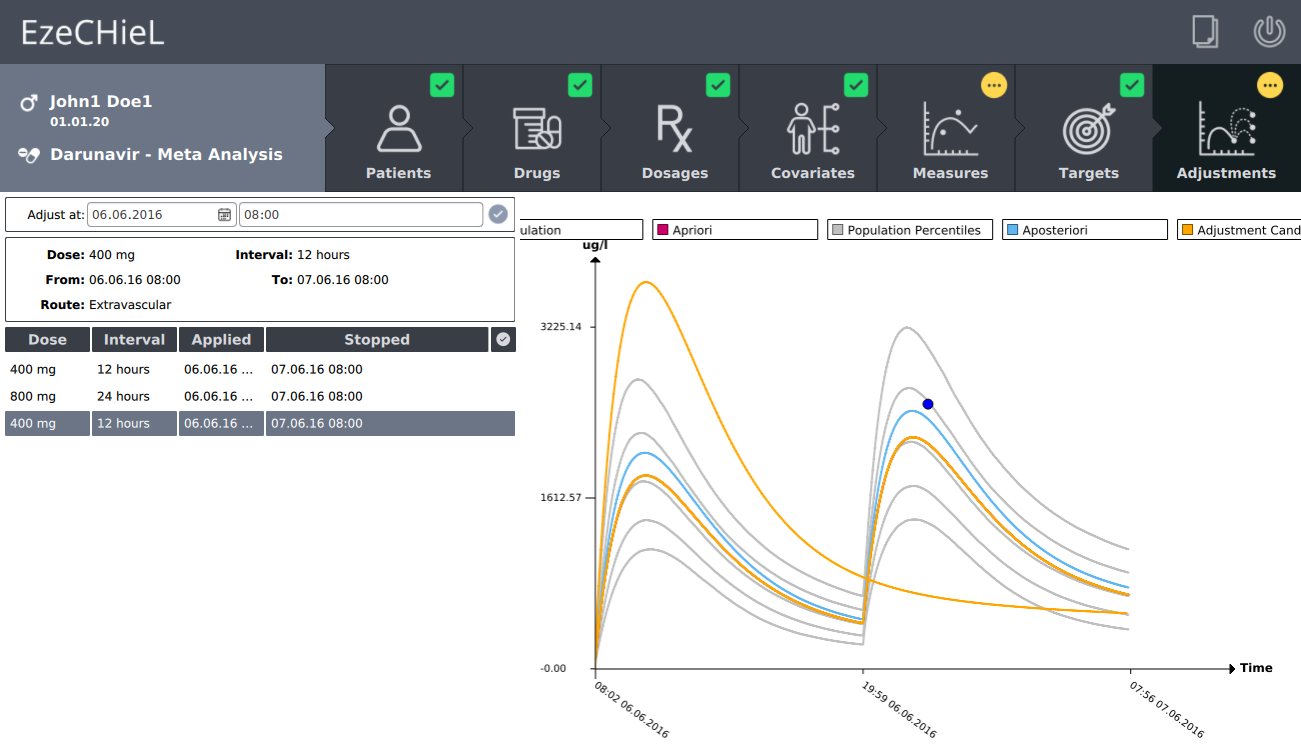
- A Bayesian calculator that allows:
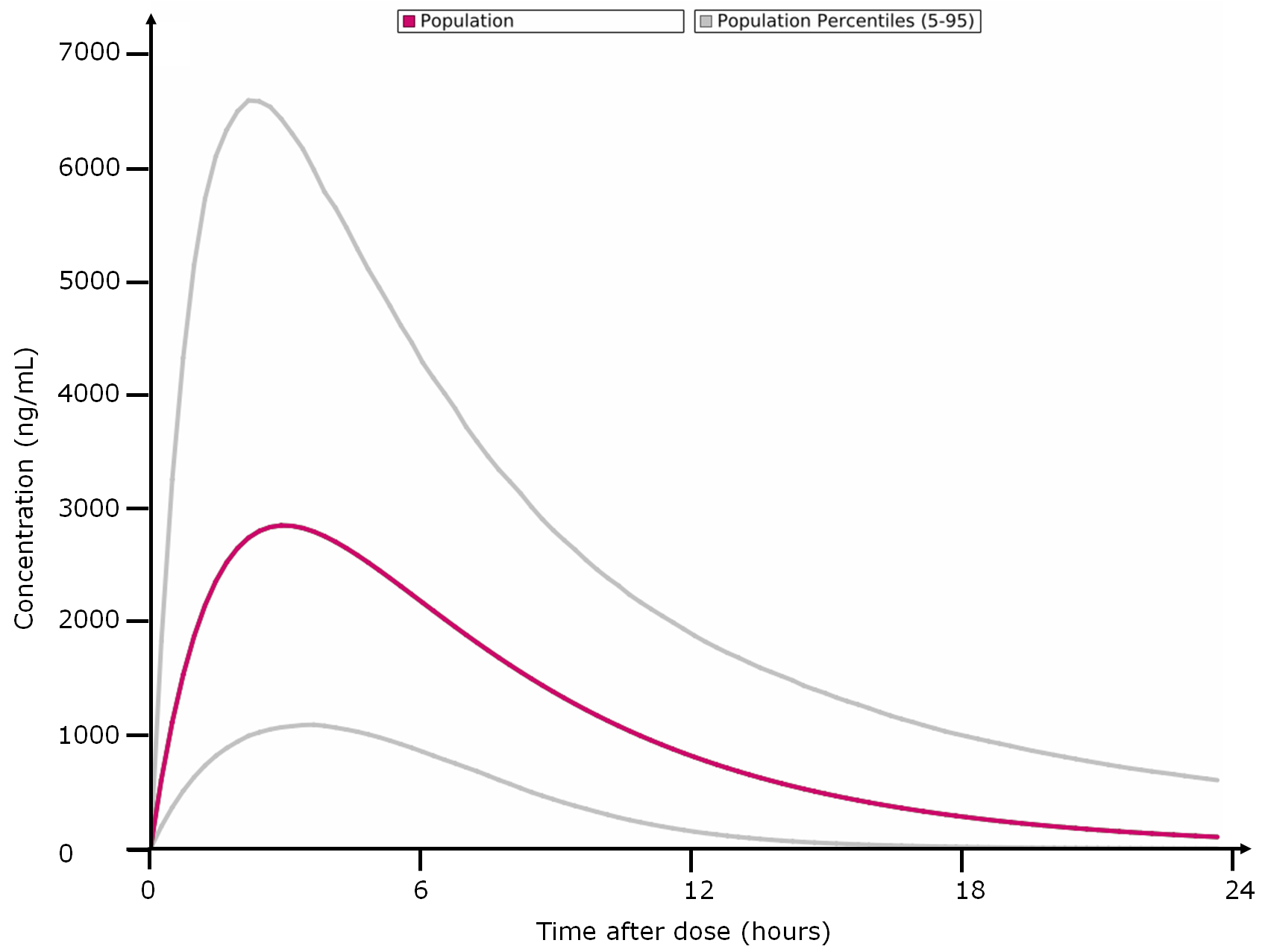
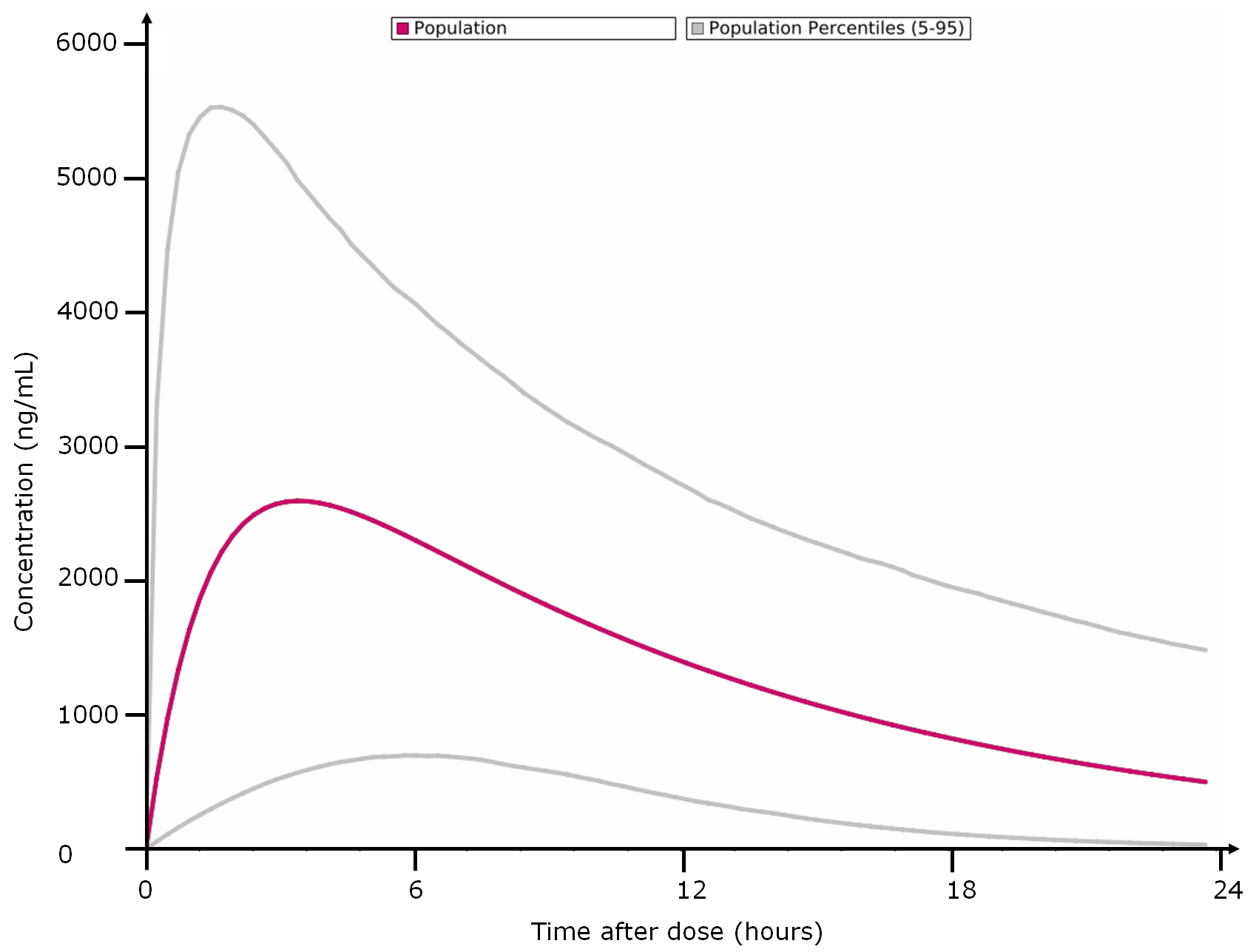
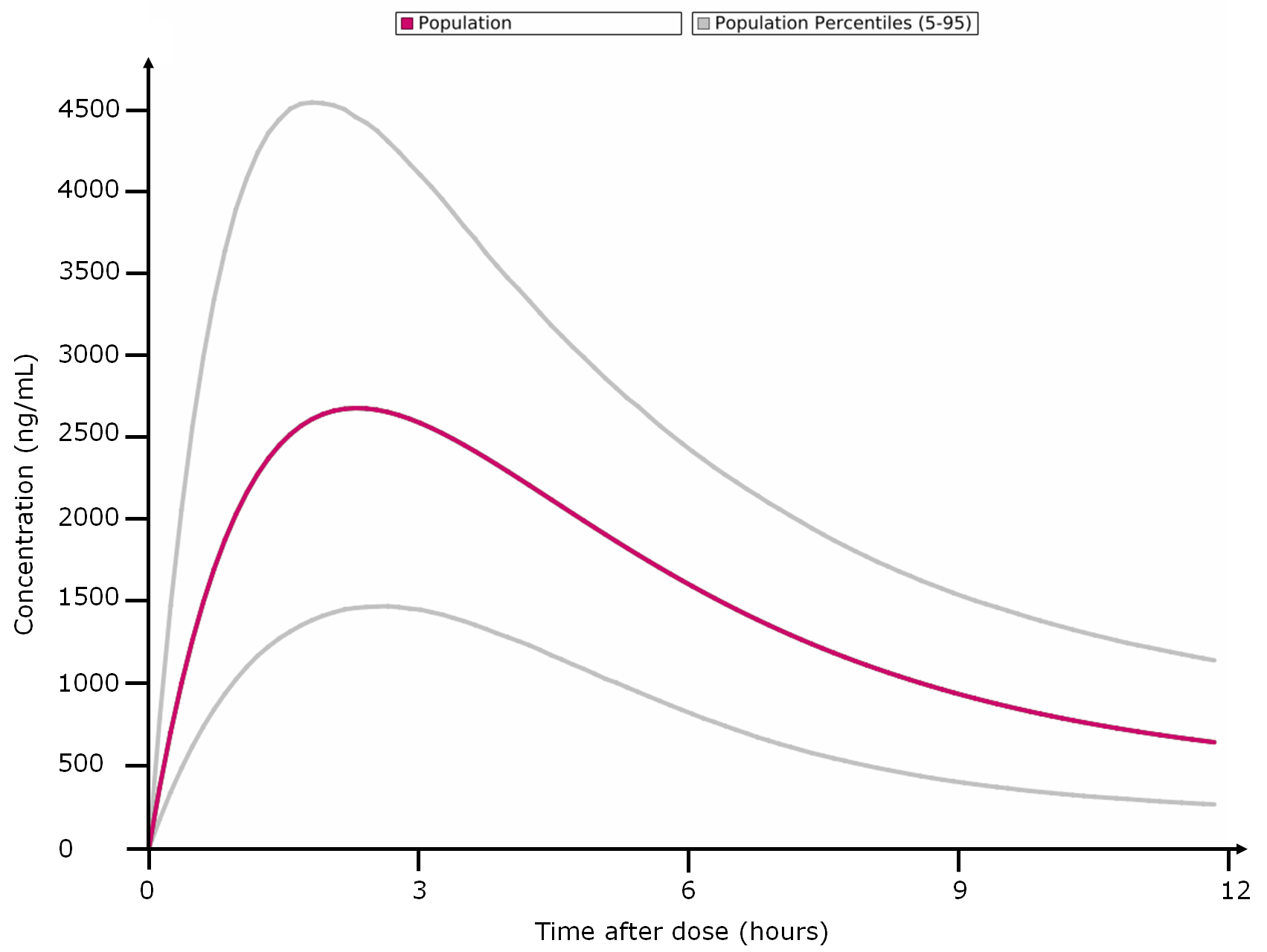
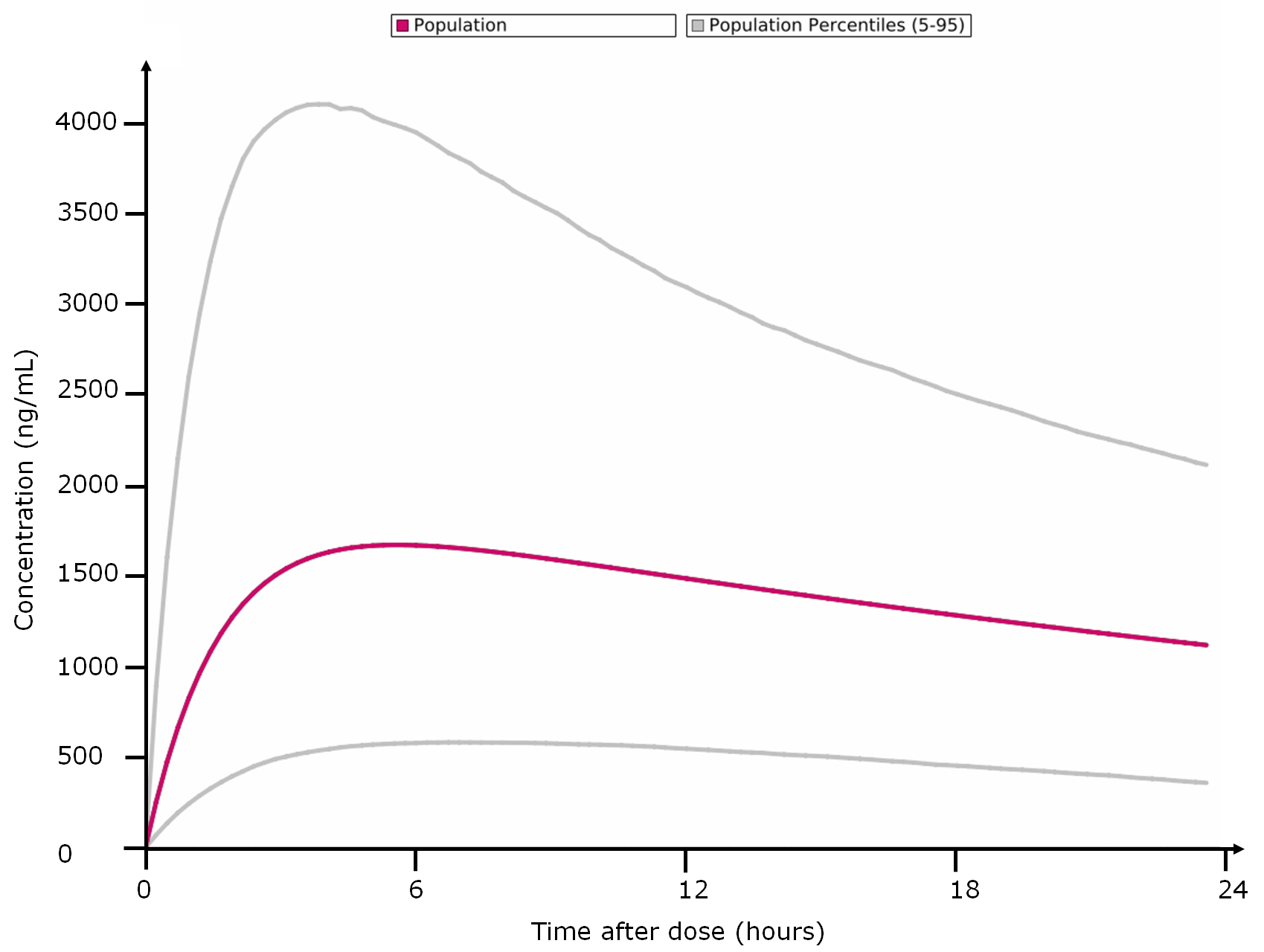
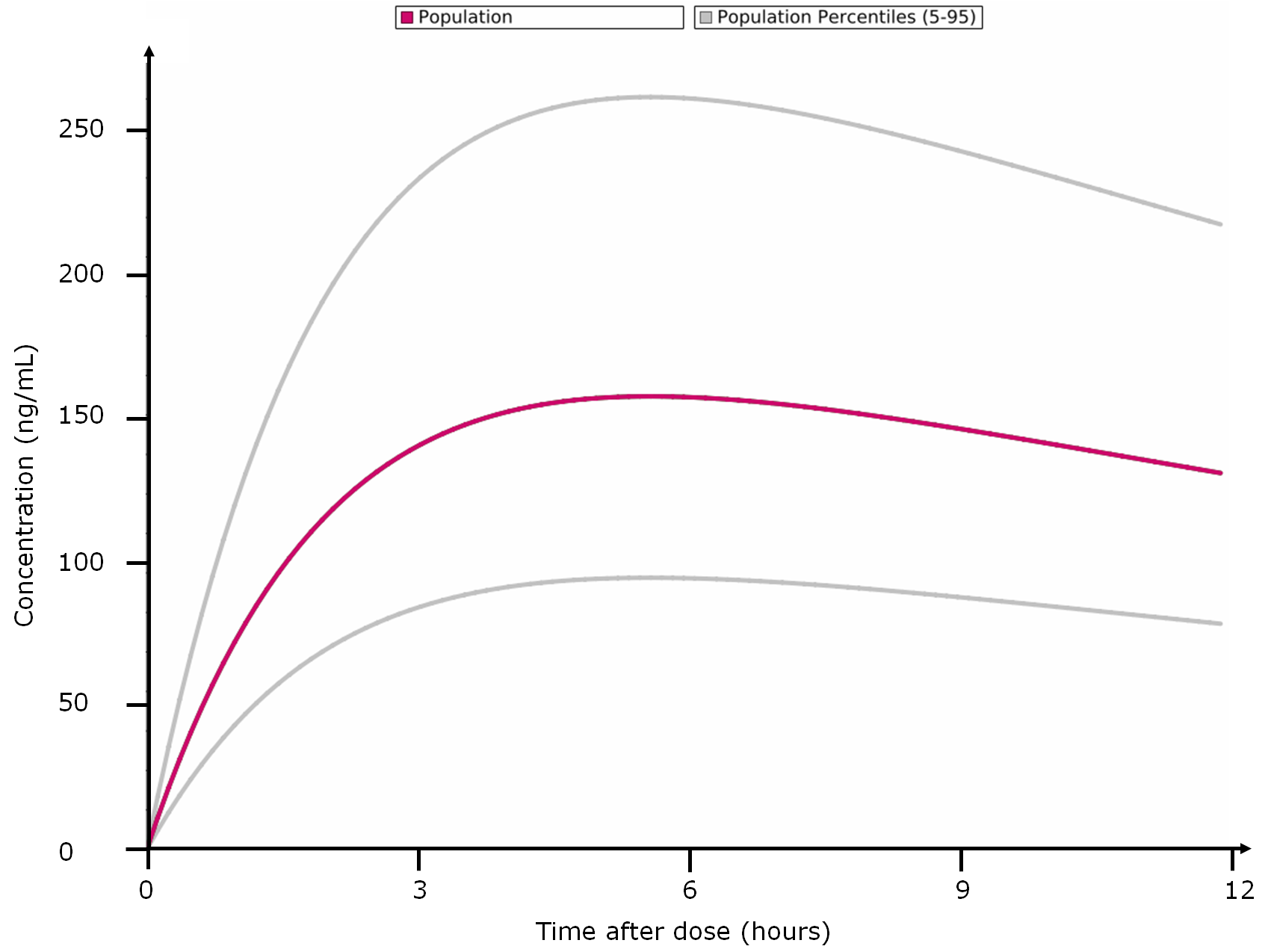
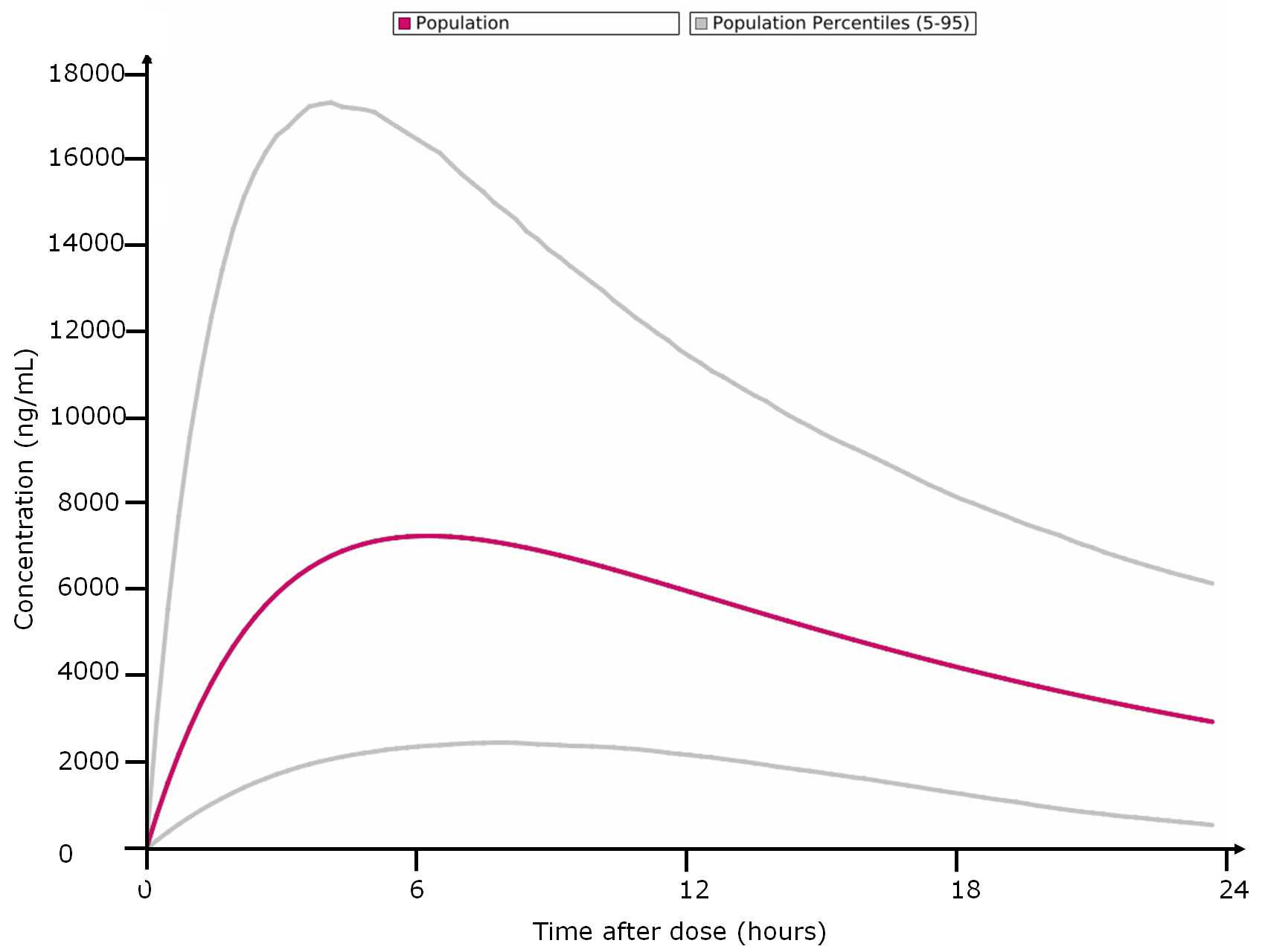
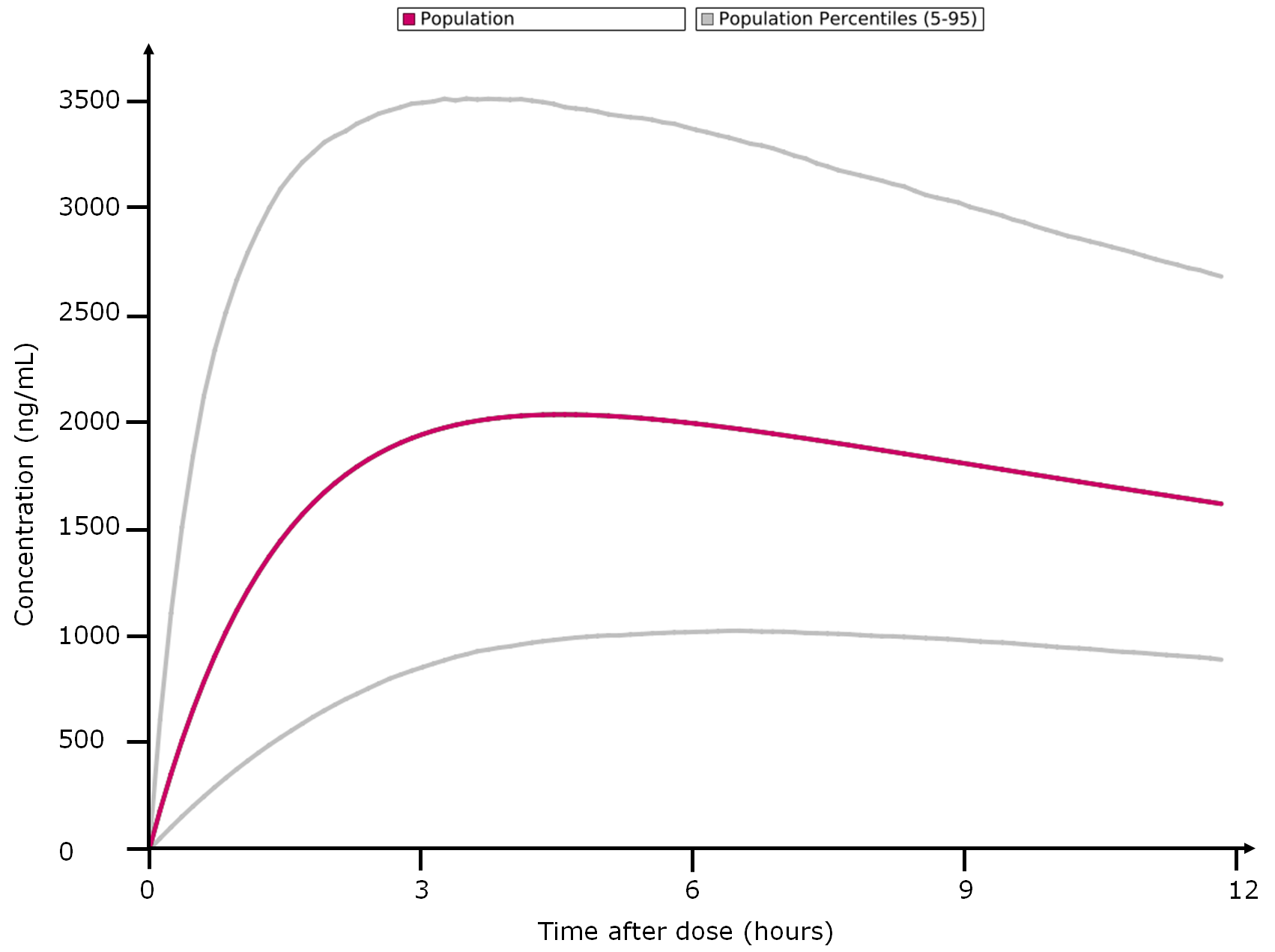
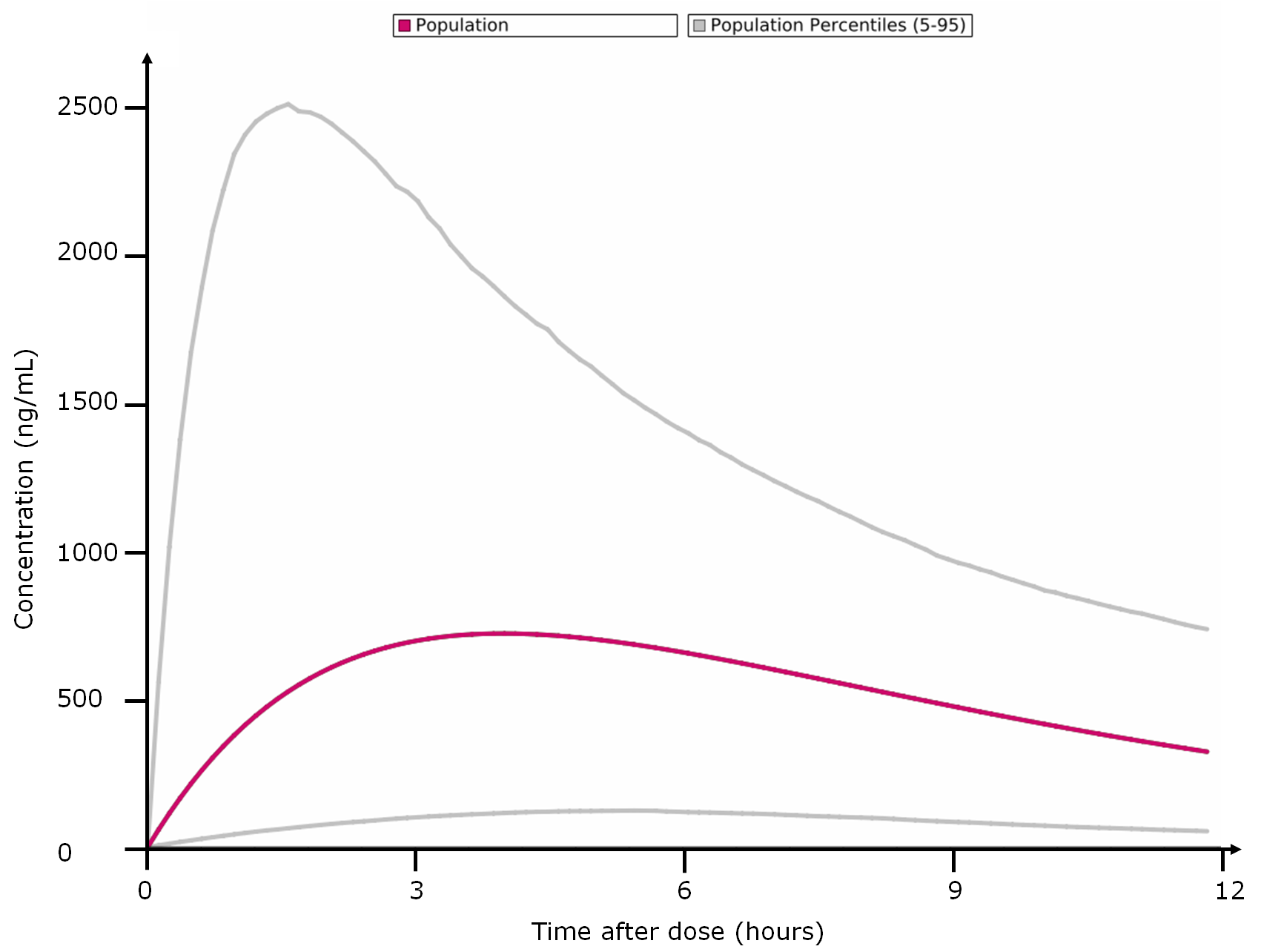
- Percentiles calculation, based on population data
- Individual parameters adjustment, based on population data and observed concentrations
- Prediction of drug concentrations
- Proposition of suitable dosages in order to reach the expected drug level
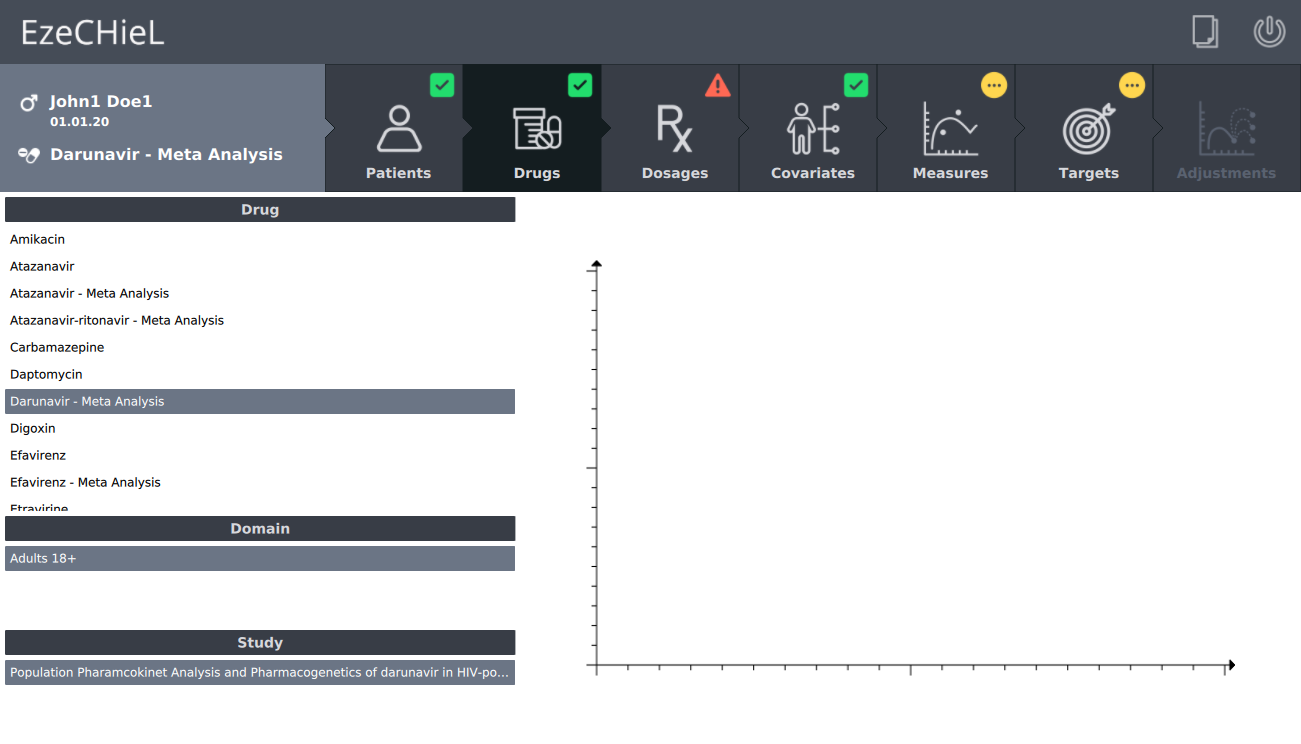
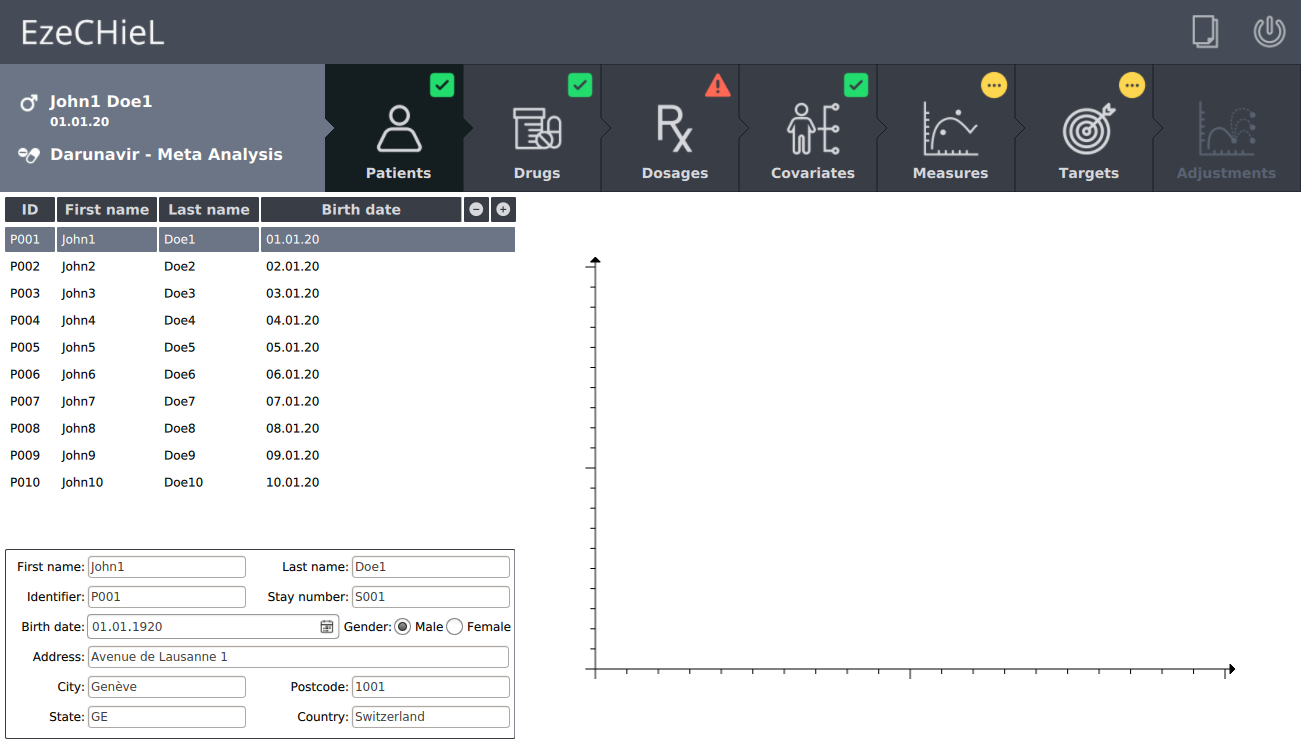
- Management of a patients database
- Generation of printable reports
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Drugs are traditionally prescribed at a standard dosage whatever the patient profile. However, critical drugs (anticancer, anti-HIV anti-epileptics…) are increasingly recognized to deserve dose individualization. Monitoring of blood drug concentration (TDM) represent the best way to optimize drug dosage and avoid toxicity or loss of effectiveness. TDM is beneficial for both patients and healthcare systems: studies have shown a reduction of mortality by up to 50%, of hospital stay length by up to 16 days per patient as well as significant cost reduction (Schumacher et al. Ther Drug Monitoring, 1998) .
About the Project
This project has been funded by the swiss nano-tera.ch initiative.  It is a subproject of two official projects: ISyPeM, and ISyPeM II. Both these projects allowed to develop new approaches for personalized medicine, with the goal of reducing the time required for medical drug blood concentration analysis. EzeCHieL was the software side of the analysis, while other subprojects were focusing on the physical blood analysis.
It is a subproject of two official projects: ISyPeM, and ISyPeM II. Both these projects allowed to develop new approaches for personalized medicine, with the goal of reducing the time required for medical drug blood concentration analysis. EzeCHieL was the software side of the analysis, while other subprojects were focusing on the physical blood analysis.